The Foundations of Blockchain Technology and Cryptocurrency
Almost everyone who uses Internet has heard about blockchain and cryptocurrencies, but when it comes to practice, a deeper knowledge is required. So if you are thinking about using blockchain and cryptocurrency for your business, this blog post will be useful for you.
What Is Blockchain
Basically, a blockchain is a decentralized ledger that records and tracks transactions. Decentralized means that a single organization or institution cannot control these transactions, thus making the transactions transparent and accessible to anyone who can access the internet. This technology is made mostly with Java, C++, and Golang as these programming languages are decently abundant in terms of run-time polymorphism and allow engineers to manage the data according to their needs. Initially, blockchain was a technology behind cryptocurrencies, but recently it has gone far beyond digital currencies and is now used by banks, governments, real estate agencies, and more.
How Blockchain Works
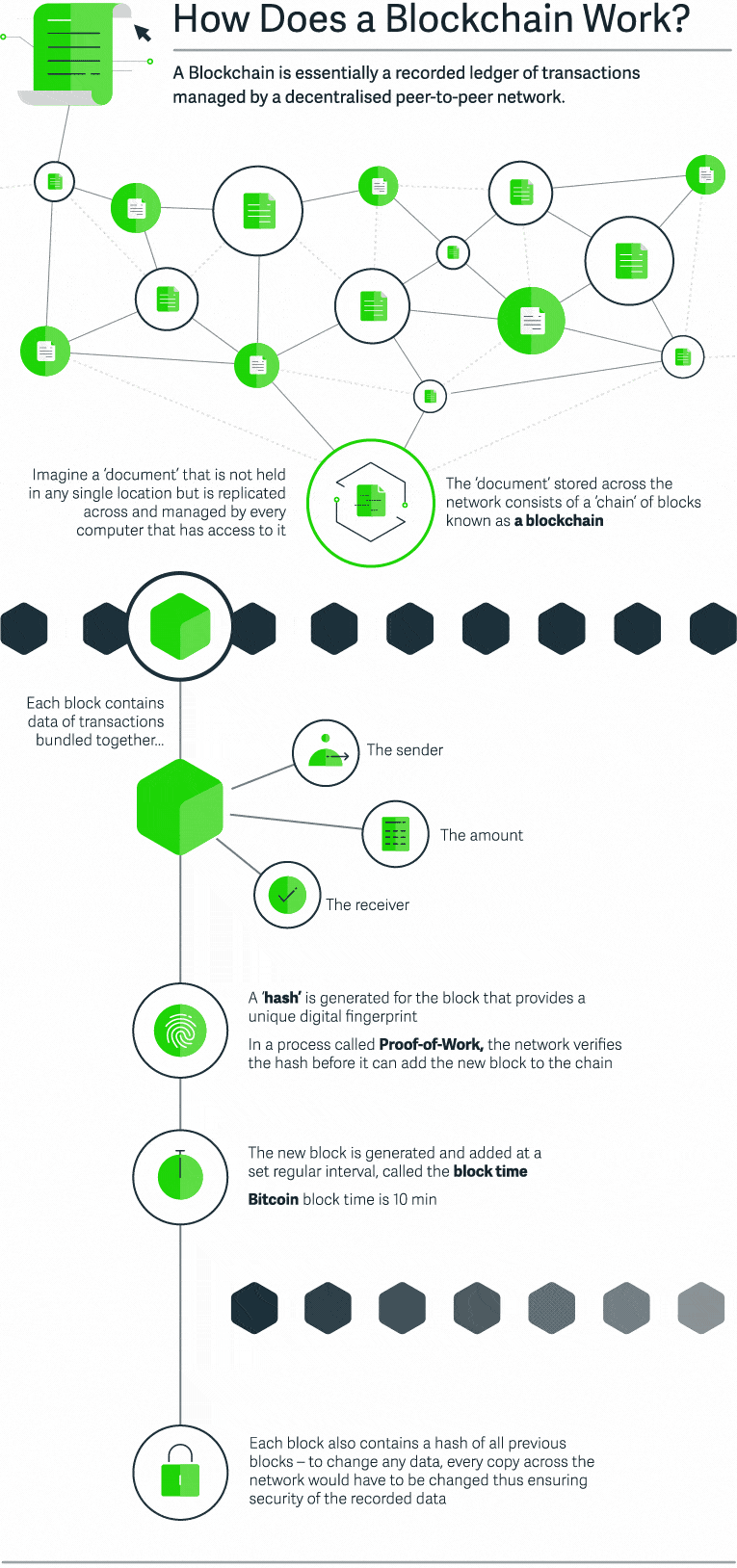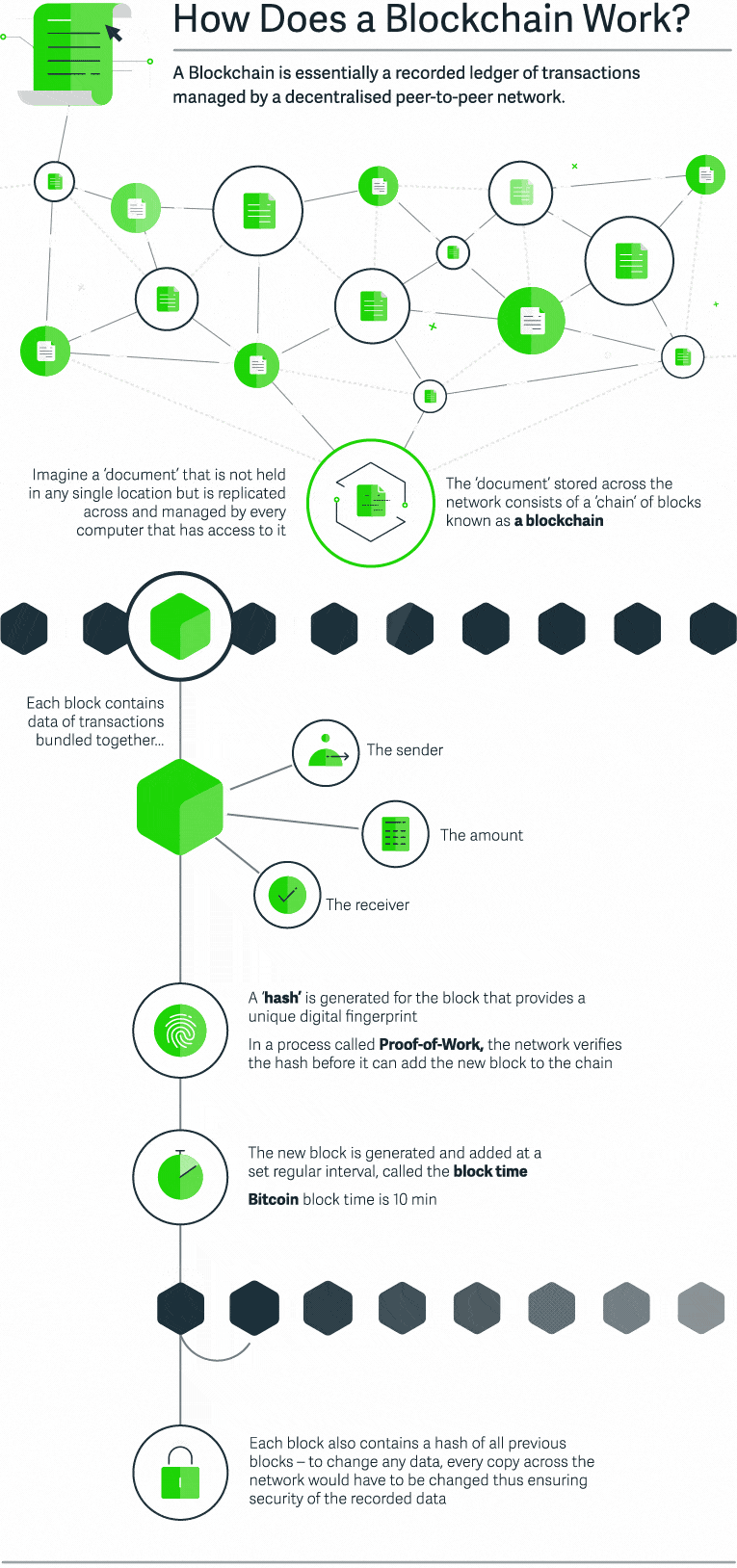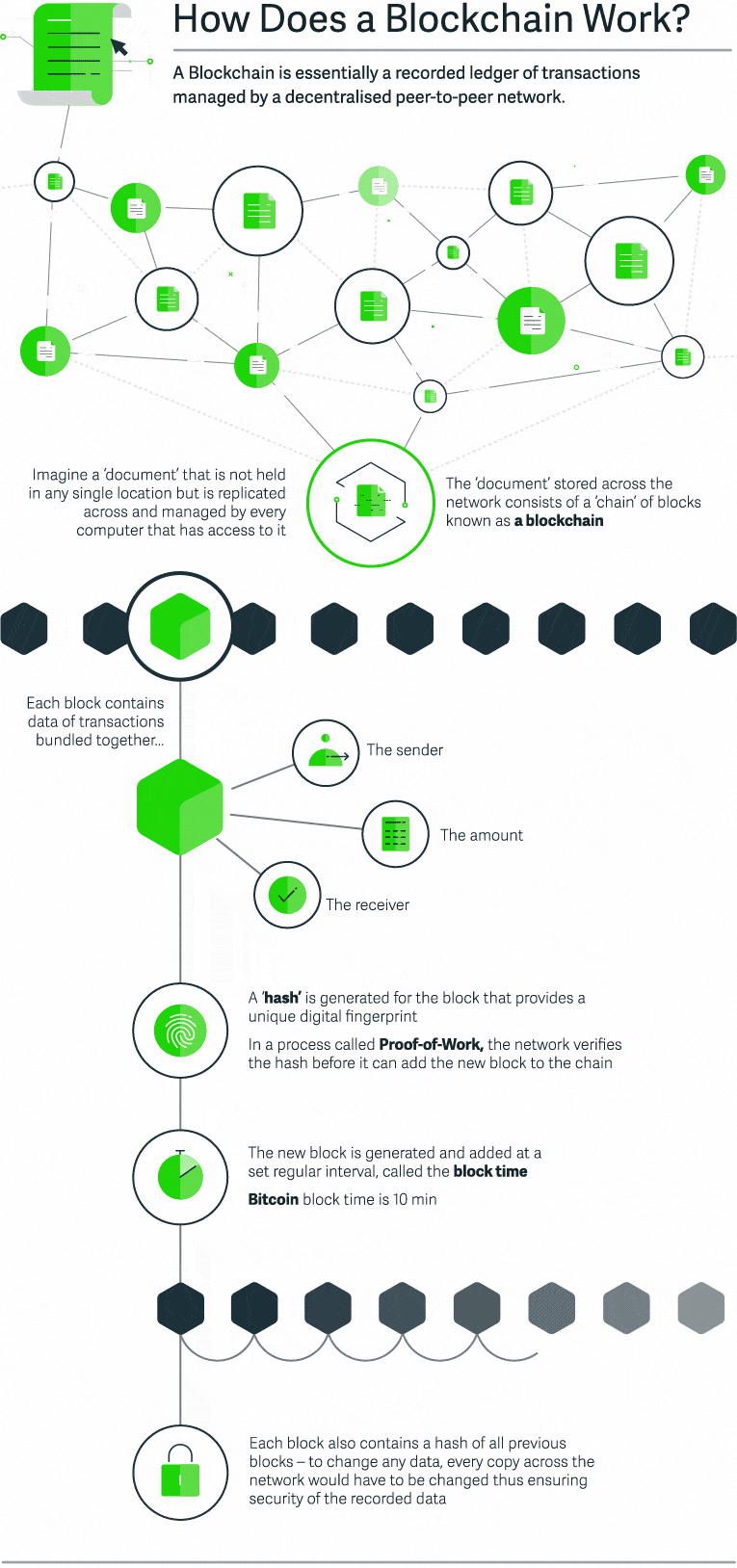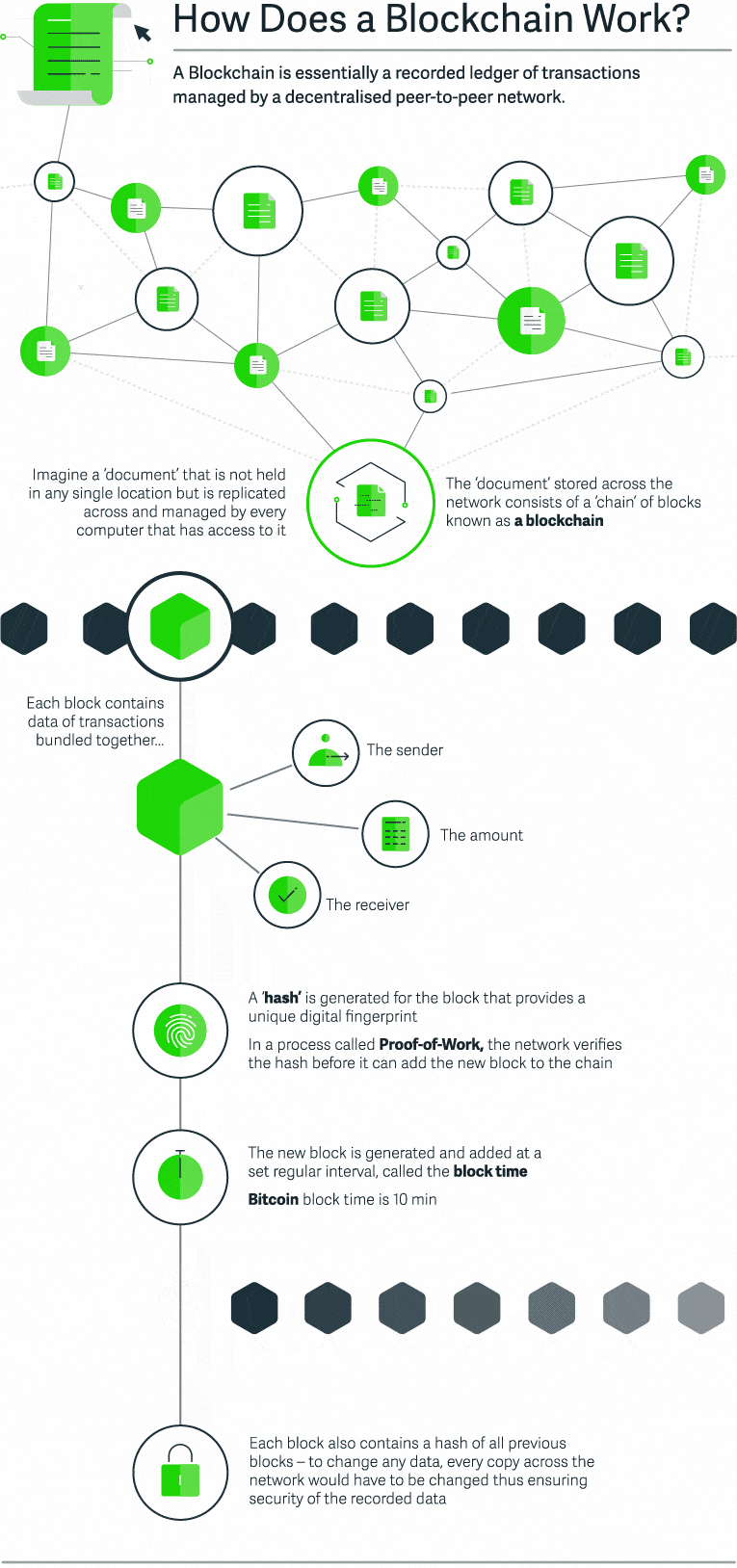
Let’s suppose that we are going to record a document with financial transaction data in the blockchain. This document is stored across the network and consists of a sequence of blocks – a blockchain. Each block contains transaction data – basically, the sender, the receiver, and the amount. Each block also has a “hash” – a digital fingerprint that is required to add this block to the chain. The blocks are generated and added at a specific time interval – block time. Finally, each block replicates the hash of all previous block. As a result, all changes to the document will be replicated for each copy of this document, thus ensuring the security of the recorded data. The level of blockchain app security goes miles ahead of other similar services.
What Is a Cryptocurrency
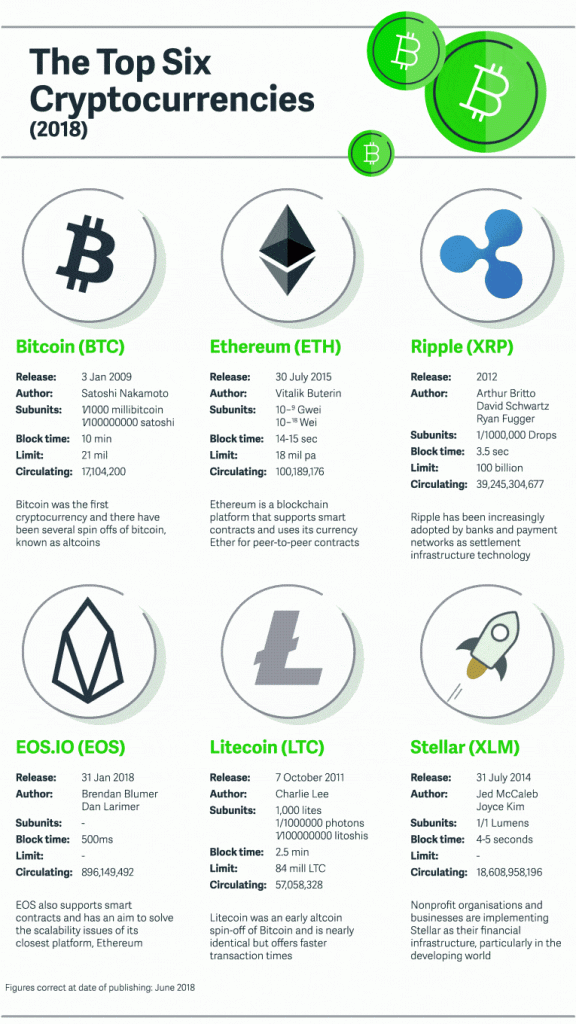
A cryptocurrency is a digital asset that records financial transactions. Cryptocurrencies use cryptography to protect financial transactions, verify the transfer of assets, and control the creation of additional units. All cryptocurrency transactions are recorded and stored in the blockchain. Digital currencies use a peer-to-peer network to prevent double spending. Currently, there are more than 1,500 cryptocurrencies in the world, but the most known and valuable are the following:
- Bitcoin (BTC). This is the first cryptocurrency that was created in 2009.
- Ether (ETH). Released in 2015, ether is the key currency of the Ethereum smart contracts platform. Smart contracts allow the users to carry out transactions without third parties.
- Ripple (XRP). This digital currency was created in 2012 and now is actively used by banks and payment networks as settlement infrastructure technology.
- Eos.io (EOS). This currency is relatively young but it already belongs to top 5 cryptocurrencies as of July 2018. It also uses smart contracts and offers the EOSIO platform that provides infrastructure for decentralized applications.
- Stellar (XLM). Created in 2014, the Stellar currency is used by non-profit organizations to manage their financial infrastructure.
- Litecoin (LTC). This is a lighter version of bitcoin that offers faster transaction times.
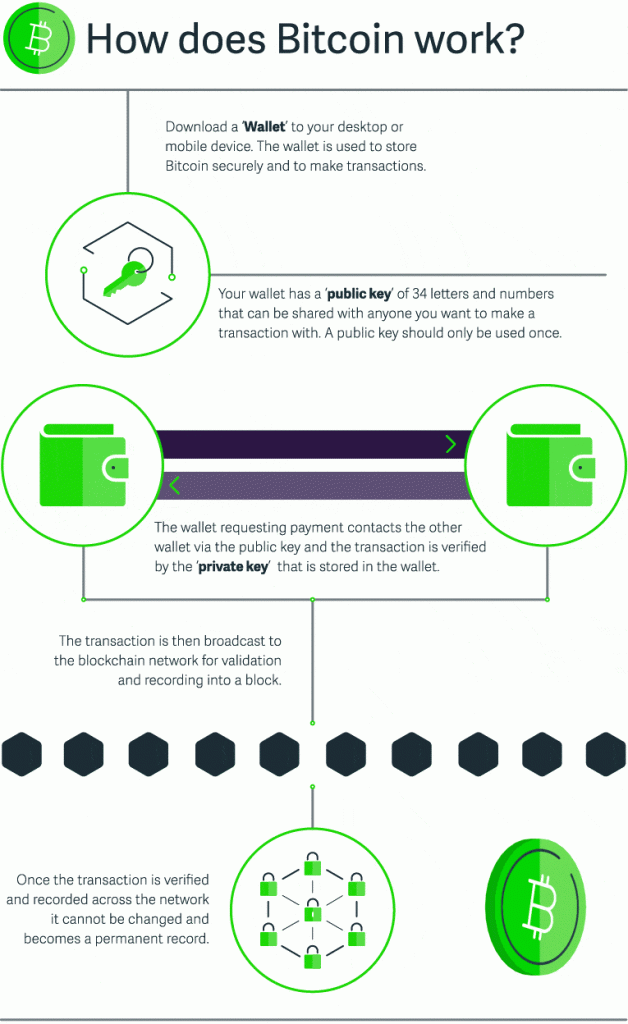
How Bitcoin Works
Now we will show you how cryptocurrencies work by using an example of bitcoin.
- First of all, you need a wallet to store bitcoins and make transactions. We recommend a desktop wallet because it is the most secure option. Your wallet should have a unique identifier – an alphanumeric “public key” that acts as an “address” for your cryptocurrency transactions.
- The wallet that requests the payment uses the public key to contact another wallet.
- The transaction is verified by the “private key” that acts as a “password” and is stored in the wallet.
- The transaction is validated by the blockchain network and recorded in a block.
- The recorded transaction cannot be modified and becomes a permanent record.
Bitcoin allows you not to link any kind of real-world identity to your account (the wallet). Anyone is allowed to create an unlimited number of wallets without revealing personal data like the name or phone number. To learn more about Bitcoin essentials, check out this article.
The original article was published on Sage Advice.