Fintech software is a fusion of emerging technologies that allow financial institutions to offer their services more quickly and efficiently to customers in a progressively mobile and web-connected world.
As the fintech industry gains momentum and companies turn to increasingly sophisticated technologies and algorithms to power their products, finding the perfect talent for a fintech project becomes one of the most critical challenges for businesses looking to ramp up their software development or modernize legacy systems.
We provide a comprehensive overview of the most promising fintech market trends, outline essential steps for fintech development outsourcing, and highlight key platforms for hiring software engineers with experience in financial technology.
Table of Contents
FinTech Industry: Market Overview and Trends
The fintech industry spans digital payments, neobanking, digital investments, and capital raising, emerging as one of the most significant trends in financial services. Consumers are increasingly using mobile payment solutions for their daily transactions, while digital investment platforms are gaining traction, offering individuals low-cost and user-friendly investment options.
Financial technology revenues are projected to grow sixfold from $245 billion to $1.5 trillion by 2030, according to a report released in May 2023 by Boston Consulting Group. The global consulting firm suggests that the fintech journey is still in its early stages and will continue to revolutionize financial services by enhancing customer experience and providing solutions to credit-starved and underserved small businesses.
In this section, we will delve into the most important trends sorted by fintech industry subcategories.
Mobile Banking
Mobile banking refers to a service provided by a financial institution that allows customers to manage financial transactions on a mobile device. The service can include managing deposits, transferring funds, paying bills, locating nearby ATMs, or receiving online help from a personal bank advisor.
These activities offer convenience to customers, as they can manage bank accounts and transactions, review expense and income statistics, and perform other financial operations with a tap of their fingers. Using a mobile app also reduces the bank’s transaction handling costs, as customers don’t need to physically visit bank branches for non-cash withdrawals and remote deposit management.
The latest trends in mobile banking include biometric authentication, AI-supported customer service, wearable banking, and advanced security measures.
Cryptocurrency/Digital Tokens
Cryptocurrencies, digital tokens, and digital cash represent one of the most dynamic areas of fintech innovation. They often rely on blockchain technology, which enables the use of so-called smart contracts – computer programs that enable trusted transactions and contractual agreements among various parties without the need of a central authority or legal system.
Blockchain technology has the potential to substantially simplify banking and reduce costs. Its capabilities vary from storing client identities and handling cross-border payments to the clearing of trade transactions.
Underpinned by cryptographic systems, cryptocurrencies allow for more affordable and faster money transfers and decentralized systems that do not collapse at a single point of failure. However, their price volatility, high energy consumption for mining activities, and use for criminal purposes limit the extensive expansion of the blockchain technology.
Insurtech
Emerging insurtech carriers and distributors are B2C startups, frequently digital brands, with the aim of transforming established insurance purchasing and pricing methods.
Tech opportunities that have the potential to revolutionize virtually every aspect of insurance include telematics, artificial intelligence, data analysis and automation with company comparison playing a pivotal role in evaluating the technological and operational performance of insurtech firms against their peers. Fintech firms also face the challenge of protecting their assets against various financial risks and uncertainties. As they innovate, incorporating effective asset safeguarding strategies becomes paramount to secure digital investments and transactions. This not only ensures regulatory compliance but shields the firm against potential litigations or financial discrepancies.
Insurtech projects venture into areas where traditional insurance companies have less leverage, such as personalized insurance policy selection, social insurance, and using data from Internet-connected devices to dynamically adjust premium prices.
Insurance technology is trying to address the challenge of data analytics by using geolocation tracking of cars and wrist-worn activity trackers. Ultimately, this approach creates more distinct risk groups, allowing for more competitive pricing of products.
Open Banking
Open banking is a practice that allows third-party service providers to access financial data from banks and other financial institutions through the use of application programming interfaces (APIs). Sharing your bank account information with another provider makes it easier to access credit and personalized offers, helps maximize savings and investments, or avoids overdraft fees by allowing the financial service provider to automatically move money between bank accounts.
One example of open banking software is Mint, a personal finance tool that connects all of your financial accounts, such as mortgages, credit cards, and online payment systems. It then allows you to analyze your money habits, automate regular payments, and monitor your credit score.
Open banking is a major source of innovation in the fintech industry. However, it is often criticized for increased security risks, as hackers can target third-party apps and trick banking customers and third-party companies with phishing scams.
Integrated Invoicing
FinTech innovation has opened doors for small- to medium-sized businesses to access more sophisticated, mobile-first products for managing money, accepting payments, and consolidating important accounting data. An example of such products includes integrated payment systems that connect critical payment processing functions with other vital business systems and software.
An illustration of such software is Tide, a UK financial technology company that offers free business bank accounts, automated bookkeeping, integrated invoicing, and connects with online accounting systems like Xero, Quickbooks, and FreeAgent.
Automated Investing/Robo-Advisors
For those unfamiliar with the technology, a robo-advisor may seem like something out of a science fiction movie. However, in the fintech industry, a robo-advisor is a digital platform that provides algorithmic financial planning and investment management. It typically offers goal planning, account services, and portfolio management at often inexpensive rates. This service does not require human intervention to provide financial assistance to the client, but it has been criticized for its lack of empathy and complexity.
According to Investopedia, the industry is experiencing significant growth, with client assets managed by robo-advisors projected to reach $5 trillion by 2027.
Key Players in the Fintech Software Industry
Global investment in financial technology has increased by more than 12,000%, from $930 million in 2008 to $121.6 billion in 2020. Implementing cloud computing, big data, the Internet of Things (IoT), and blockchain, the fintech industry has produced various innovative products over the past ten years.
In addition to cloud computing, blockchain, and mobile development, artificial intelligence (AI) is playing an increasingly important role in fintech software. For example, AI-powered voice recognition and facial scanning are used to manage financial accounts and detect fraud. AI algorithms also provide companies with insights into customer purchasing habits by processing large amounts of financial data. Finally, AI-powered robo-advisors can help customers effectively manage their investments.
The digital payment systems market, a colossal and hyper-competitive fintech subdivision, has witnessed the rise of numerous companies – from PayPal, which introduced the first version of its electronic payment system as early as 1999, to international powerhouse Stripe, providing APIs that developers can integrate for payment processing into their websites and mobile apps.
Another flourishing area is neobanks, which are fintech products that usually have their own banking licenses and challenge traditional banks by exclusively operating through online services.
A notable example is the Ukrainian neobank, Monobank, which became a harbinger of fintech’s emergence in 2018 by offering payment services, microlending, and deposits through a mobile application. Since then, its number of active customers has grown to 7.5 million, and it has expanded its features, allowing customers to open business accounts, accept credit card payments without a card reader, and purchase S&P 500 stocks or funds. In 2023, Monobank appeared on the list of the world’s top 200 fintech companies compiled by CNBC and the independent market research firm Statista.
Wealth management companies such as Robinhood and Betterment have also grown in recent years, lowering the barrier to entry for people who want to own stocks and other assets and build their portfolios. While interest from amateur traders has declined since the retail investing boom of 2020 and 2021, these companies continue to attract customers by providing opportunities to invest in government bonds and other high-yield savings options. They are also expanding their influence in digital asset management.
2021 was Robinhood’s most successful year, when the company listed its own shares on the Nasdaq. In 2022, the startup gave its customers access to a crypto wallet, allowing them to move crypto in and out by buying and selling assets, as well as spend crypto on actual products. The same year, Betterment launched their crypto offering, which enabled customers to invest in curated selections of digital assets.
What is Fintech Development Outsourcing?
Outsourcing is a business practice that involves hiring an external vendor to handle a planned or existing fintech project that was traditionally carried out in-house by the company’s own employees. Fintech companies choose outsourcing to reduce development costs, relieve the in-house team of additional responsibilities and non-essential tasks, or access software engineers with specific skill sets and experience that may not be widely available in the local market.
Fintech businesses outsource software development to build, deploy, and maintain custom solutions in the following categories:
- Online Banking
- Payment Gateways and Digital Wallets
- Blockchain
- Investment Management
- Personal Finance
- Financial Data Analytics
- Trading and Exchanges
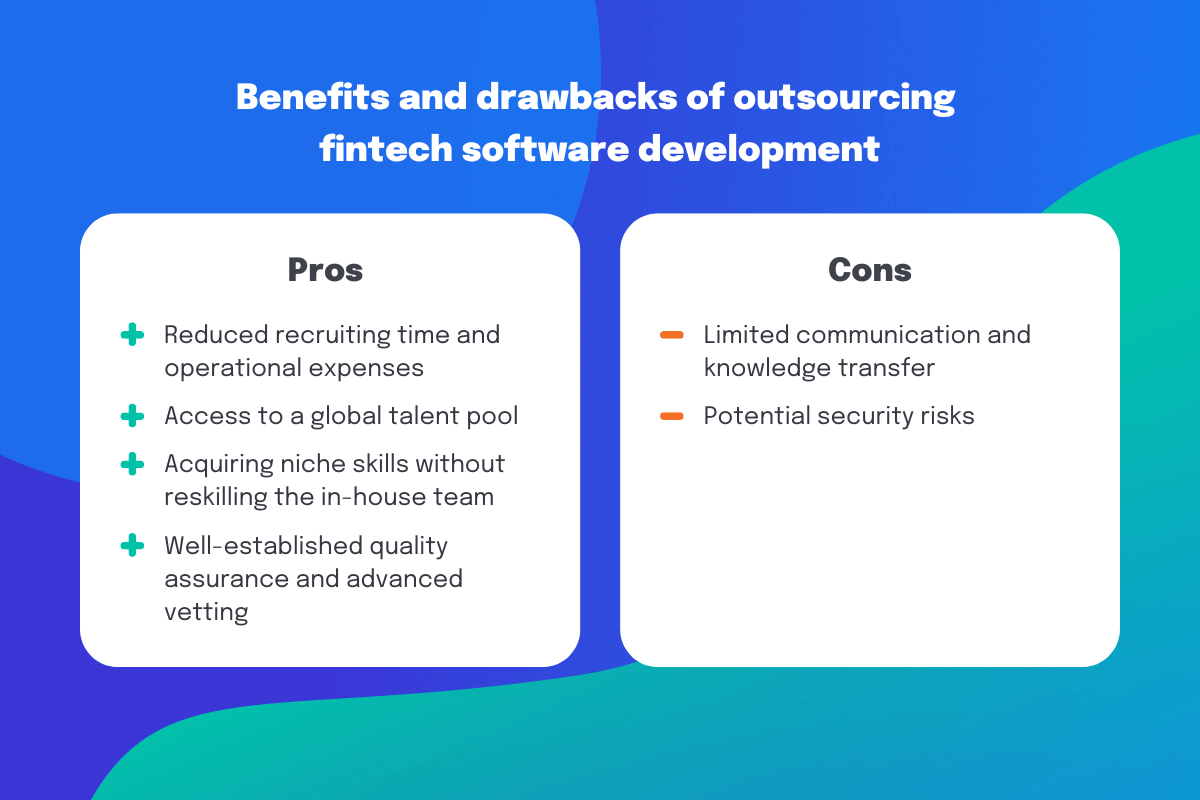
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Outsourcing Fintech Software Development?
Here are the most crucial reasons why companies choose outsourcing:
- Cost efficiency: Fintech companies turn to outsourcing to cut recruiting and administrative costs. Hiring an external provider also allows companies to focus on the core aspects of their business, spinning off the less critical operations to outside vendors.
- Flexibility: With outsourcing, companies can ramp up their development to keep up with demand for the product, without the financial commitment of hiring in-house employees, the cost of which can take years to pay off.
- Access to a global talent pool: Outsourcing fintech software development implies connecting with the rich talent pool and finding the ideal candidate with the required skill set, domain expertise, and professional preferences.
- Tapping niche skills without reskilling your in-house team: It can take months and even years for internal teams to learn niche disciplines such as machine learning, data science, and master specific services such as cloud migration and automation of banking and finance processes. Outsourcing immediately opens the way to professionals with robust experience in these fields.
- Improved quality: Outsourcing companies have well-established quality assurance guidelines and procedures. In addition, outsourcing vendors can bring a fresh perspective to software development and help fintech companies find new ways to improve their products and services.
However, along with the advantages of outsourcing, there are also some downsides that we should warn you about:
- Security risks: Transferring knowledge and design documentation to an external provider can be risky if the outsourcing company doesn’t have strong security measures in place. Data security and compliance are especially important for fintech companies that handle sensitive financial data.
- Limited communication and knowledge transfer: If the provider does not maintain clear project documentation, you may come across some features or scripts that are unclear to you. In addition, hiring offshore developers requires management attention during onboarding to align workflows and establish communication between in-house and remote teams.
A Step-by-Step Guide for Fintech Development Outsourcing
In this section, we provide the most crucial steps for companies that are outsourcing their fintech project development.
Step 1: Conduct Market Research and Brainstorm Ideas
Before outlining a fintech project’s requirements, companies should conduct market analysis and UX research to find out what the end users of a service or product need and want. Financial organizations also perform business analysis to identify growth points and brainstorm ideas to determine what makes the software different from the competition.
Step 2: Define the Fintech Project Goals and Requirements
The fintech development project description and requirements include a summary of objectives, disciplines, tools, and frameworks to be used and define a desired set of skills, experience, and education. The company’s technical leads and hiring managers should also define performance-based requirements to set clear expectations for the outsourcing vendor.
Step 3: Decide on the Budget
Identify the number of professionals to be hired, their rates or salaries, and consider the commission of the hiring platform or outsourcing vendor.
Step 4: Research the Outsourcing Companies and Hiring Platforms
Visit review websites and online platforms for hiring developers and development teams to find the exact talent you need for your fintech project, according to its timeline and requirements:
- YouTeam: A staff augmentation marketplace where you can hire full-time vetted contractors;
- Upwork, TopTal: These platforms are suitable if you’re looking to hire freelance fintech app developers, architects, and consultants;
- G2, Clutch: Review websites where you can find an outsourcing provider and either assign the entire project to them or hire a dedicated team.
Step 5: Create a Shortlist of Outsourcing Vendors
Before deciding to reach out and sign the contract with an outsourcing development agency, you should focus on their portfolio, domain expertise, and customer reviews. You should also check whether the outsourcing company or marketplace adheres to security standards and contractual agreements on intellectual property transfer and data protection.
In addition, you should make sure that the outsourced provider adheres to the latest practices in software development and is able to build reliable systems to verify identity, protect user data, or secure information they may exchange in the built-in chat.
After reviewing the aforementioned criteria, you will narrow down the shortlist of the most suitable development companies with expertise in fintech industry projects.
What Are the Different Options for Hiring Fintech Software Developers?
Hiring Fintech Developers: Options Based on Geography
Depending on the geography, there are three options for hiring fintech developers: companies can find local talent, hire a nearshore software engineer, or outsource to an offshore developer. The latter two options are more often used in the context of outsourcing, while hiring local talent is more likely to involve traditional recruitment.
Hiring Nearshore and Offshore Fintech Developers
Nearshore and offshore outsourcing gives fintech companies access to a large pool of developers, helping to fill skill gaps when the required talent is not widely available in the local market. Unlike in-house hiring, outsourcing reduces administrative and recruiting costs and relieves the company of the commitment to integrate new specialists into the internal team and develop a long-term strategy for their professional development.
The hiring process for both options is quite similar. You can visit B2B rating platforms such as G2 and Clutch and look for development companies or hiring platforms with good customer reviews. In addition, companies can find development agencies by attending regional events such as tech conferences and meetups.
Hiring Local Fintech Developers
Hiring local talent usually means that developers join your team and work in the same office. This allows closer communication between development team members and other teams.
When we talk about hiring local developers, we usually mean traditional hiring methods, such as searching for candidates on LinkedIn or browsing job boards like Wellfound or Glassdoor.
You can also search for developers by hosting or attending local hackathons and tech conferences, as offline events seem to be picking up pace after the COVID outbreak. Finally, you can request an in-house fintech developer from headhunting firms.
Hiring Fintech Developers: Which Hiring Model Best Suits Your Project?
Staff Augmentation
Staff augmentation is a hiring practice for financial companies that need to quickly expand their development team with additional talent or find niche skills unavailable in the local market. This option utilizes already vetted software engineers employed by development agencies and helps companies not worry about operational and administrative costs.
As with in-house developers, companies manage contract developers and communicate directly with each one. In addition, team augmentation is as secure as in-house hiring, as it typically offers standardized, locally-compliant contracts, risk-free trial periods, safe intellectual property transfer, and data protection.
However, staff augmentation requires management attention during onboarding to align workflows and establish communication between in-house and remote teams.
Outsourcing
If a company chooses to outsource fintech project development, it contacts an agency, evaluates the quality of engineering talent, and agrees on the project requirements and goals. Then, an outsourced development team will work on the project remotely.
Tech companies use this business practice to focus on the core aspects of their business, assigning fintech app development, deployment, and maintenance to outside organizations managed by the CTO or product owner of the in-house team.
However, outsourcing limits communication and knowledge transfer between the company and external provider. If the provider does not maintain clear documentation, you may come across some features or scripts that are unclear to you.
Freelancing
Companies typically hire freelance developers and consultants to complete small tasks. The main advantage of hiring freelancers is that there are numerous platforms like Upwork with thousands of specialists readily available to be involved in the fintech project.
However, even though freelancers are the fastest employment type, this hiring model comes with the risk of project delays and cancellations. In contrast to dedicated outsourcing teams and contractors, freelancers often juggle multiple projects, and the quality of their work may not meet the client’s expectations. Tech companies don’t have the same level of control over a freelancer as they do with an employee or a full-time contractor.
In-House Hiring
Companies prioritizing faster team communication may prefer to retain all developers in-house. In addition, in-house hiring is the most common option during the core development stage. Internal employees delve into the fintech product details and develop the best solutions because of their commitment to the company’s long-term goals. Finally, if a fintech project requires the highest level of confidentiality and security, the company may hesitate to discuss these issues with an outsourcing vendor and choose to keep the project knowledge base within the internal team.
However, this type of hiring can be time-consuming because, in addition to candidate requirements, companies should create a detailed onboarding and career development plan for in-house employees and align the company’s long-term goals with each candidate’s skills and preferences to ensure their expertise will be helpful in future projects.
How Much Does It Cost to Hire a Fintech Developer?
We analyzed the technical skills most frequently used in fintech development. The figures below reflect the average hourly rates of software developers registered on the YouTeam platform who have specified a particular skill or discipline as their primary specialization.
| Ukraine | Poland | Colombia | Mexico | |
| Blockchain Engineering | $70 | No data | $61 | No data |
| Cloud Engineering | $56 | No data | No data | $68 |
| Data Analysis | $62 | No data | $54 | $50 |
| Golang | $53 | $53 | $55 | $51 |
| Python | $49 | $61 | $54 | $53 |
| Rust | $58 | No data | No data | No data |
| Java | $48 | $62 | $51 | $51 |
| C++ | $51 | $66 | $64 | $56 |
| .NET | $48 | $57 | $53 | $52 |
| Node.js | $50 | $53 | $53 | $51 |
*Average hourly rates. Source: YouTeam.
We have also calculated the cost of hiring software developers registered on the Upwork platform. The following numbers represent the average hourly rates of top-rated engineering talent available for contract-to-hire with a job success rate of 90% or higher, earnings of $10,000 and above, and a fluent level of English.
| Ukraine | Poland | India | United Kingdom | United States | |
| Blockchain Development | $58 | $85 | $42 | $80 | $92 |
| Cloud Engineering / DevOps | $48 | $70 | $46 | $77 | $140 |
| Data Analysis | No data | $72 | $50 | $95 | $120 |
| Golang | No data | $122 | $65 | No data | $137 |
| Python | $45 | $69 | $39 | $70 | $90 |
| Rust** | $53 | No data | $89 | No data | $60 |
| Java | $47 | $60 | $40 | $60 | $90 |
| C# | $44 | $55 | $35 | $72 | $82 |
| .NET | $41 | No data | $35 | No data | $85 |
| Node.js | $42 | $59 | $40 | $62 | $91 |
*Average hourly rates. Source: Upwork.
**Please note that there are very few Rust developers, including those with blockchain experience, registered on the Upwork platform. Therefore, the actual average hourly rates of Rust developers may differ significantly from the rates shown in the table.
Where to Hire Fintech Software Developers?
We provide four hiring platforms for financial organizations that need to rapidly scale up or down their development team, find professionals with niche skills, and delegate non-essential tasks to outside vendors.
1. YouTeam
YouTeam helps fintech companies quickly scale up or down software development teams. The platform is a single point of access to a combined talent pool of hundreds development agencies located in Eastern Europe and Latin America. Before adding the software agency to the network, YouTeam meets with its C-level executives and project managers, while its legal team runs compliance checks into the agency’s background, legal records, and previous clients. Such a comprehensive approach to vetting agencies is especially appreciated by companies and managers who may not have much experience with contracting, as it provides them with greater confidence in their choice.
In addition to vetting their partner agencies, YouTeam conducts interviews and in-depth screening of potential candidates. Each client is assigned a matching expert who stays with the client throughout the entire collaboration with contractors. This expert assists with onboarding, scaling the team up or down, managing replacements, and evaluating the performance of software engineers. The platform also automates contract signing and billing between clients and development agencies.
Financial organizations that have chosen YouTeam as their contracting partner include StratiFi, Maxwell, Tide, HMBradley, Flutterwave, and Payscout.
2. Arc
Arc.dev grew out of Codementor, an online platform for software development mentorship. Built on top of the vibrant Codementor community, Arc helps to find and hire software developers and IT consultants.
Hiring options include permanent full-time engineers and part-time freelancers. The vetting process involves software engineers recording a self-introduction video, which Arc then reviews for English proficiency and communication skills. In addition, the platform’s engineering talent undergoes technical interviews and pair programming sessions.
Finally, the platform assists with onboarding and conducts regular reviews of developer project statuses to ensure that performance meets their quality standards. According to its website, most Arc developers are located in the U.S., Europe, and Latin America.
3. Toptal
Toptal is a freelancing platform that connects businesses with software engineers, finance experts, product managers, and project managers. The vetting process includes a comprehensive language and soft skills interview, and a technical interview to assess problem-solving abilities, critical thinking, and technical knowledge. Additionally, each candidate undergoes live tests to evaluate their coding experience and completes a real-world test project.
The platform assigns an industry expert to the client to understand their goals, technical needs, and team dynamics. This expert then accompanies the new developer throughout the trial period to ensure they are the best candidate for the role before signing a contract.
4. Turing
Turing is a platform that offers full-time contractors and managed development teams. Its features include automatic time tracking, virtual daily stand-ups, and time zone management to give clients more visibility into remote fintech developers’ work.
The company tests software engineers for English fluency and technical knowledge. Each developer also undergoes an automated work experience survey comprising questions in five areas — project impact, engineering excellence, communication, people, and direction.
Most of Turing’s clients are located in the U.S. and operate on PST (Pacific Standard Time). Therefore, the platform’s developers are required to have a 4-hour overlap within this time zone to ensure they can promptly respond to messages and participate in calls with the internal team during the workday.
In addition to finding contractors that meet specific job requirements, Turing offers IT services such as cloud migration, data engineering, AI implementation, and application assessment.
Where to Find Fintech Software Developers: A Comparison of Hiring Platforms
| YouTeam | Arc.dev | Toptal | Turing | |
| Pool of developers | Full-time employed engineers from software development agencies | Part-time freelancers, full-time contractors | Freelancers | Full-time contractors, managed teams |
| Pricing | YouTeam’s commission is 10% of the developer’s rate.
The average rate of a senior engineer is $60/hour or $9K/month. |
A custom fee per hire.
Permanent contractors’ yearly salaries range from $50,000 to $200,000. Freelance contractors’ hourly rates range from $60-$100/hour. |
Developers’ hourly rates range from $100-$150/hour.
Requires an initial deposit of $500 as a credit to the first invoice once you make a hire. The deposit is refundable. |
Turing’s service fee (TBD) |
| Geography | Developers located in Latin America and Eastern Europe | Most of the developers are located in the U.S., Europe, and Latin America. | Most talent located in the Americas and Europe | Worldwide |
| Vetting | – Compliance checks into each agency’s background, legal records, and previous clients
– English pre-interview – Soft skills interview – Tech interview – Verifying the skillsets through HackerRank for Work |
– Application screening
– Coding assessment – Hands-on project – Behavioral interview – Technical interview with a senior engineer |
– Language, personality, and communication interview
– Technical interview – Live tests to evaluate coding experience – Real-world test project |
– Automated technical skills test
– English proficiency test – Communication skills interview |
| Quality guarantee | Risk-free 1 month trial period | – Risk-free trial period of up to two weeks (for freelance positions)
– 3-month guarantee (for permanent roles) with the option to be matched with another developer free of charge |
Trial period of up to two weeks | Risk-free two-week trial period |
| Time to get a verified list of candidates | 2 business days | 3 days | Several days | 3 to 5 business days |
| Time to contract | 1 week | 2 weeks for full-time roles;
24-72 hours for hourly contractors |
0-3 weeks | No data |
How to Hire Fintech Developers with YouTeam?
The process of hiring fintech developers with YouTeam looks like this:
- You request a call and describe your fintech development project and vision of the ideal candidate.
- Your Matching Expert creates an Ideal Candidate Profile that meets your criteria, such as tech stack, industry experience, and professional development preferences.
- Alternatively, if you don’t have enough time to make calls, you can start with our AI assistant, which will gather all the necessary information to find and screen candidates.
- YouTeam finds suitable fintech developers among hundreds of partner agencies. Our experts pre-screen talent to create a shortlist of candidates who most closely match your Ideal Candidate Profile. The first batch of profiles will be ready in 48 hours.
- You receive and review your candidate shortlist and select which software engineers you want to interview. If you are not satisfied with your shortlist, the Matching Expert will source new candidates.
- The final stage is contract signing. YouTeam contracts are locally-compliant and standardized, saving you time in case of hiring several developers from different agencies.
- The platform ensures secure intellectual property (IP) transfer and guarantees the implementation of technical and organizational security practices against unauthorized processing of personal data.
- YouTeam also offers free replacements, a 1-month risk-free trial period, and a money-back policy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Pros and Cons of Outsourcing Fintech Software Development?
Outsourcing can bring innovation to legacy systems, lower the costs of software development, reduce recruiting time and operational expenses, and, most importantly, provide fintech companies access to a larger talent pool. Additionally, outsourcing is used when a fintech company needs to find professionals with niche skills such as machine learning and data science, without having to reskill their in-house team, which can take months or even years.The downsides of outsourcing are that it may limit communication and knowledge transfer, and it can be risky if the outsourcing company doesn’t have strong security and compliance measures in place.
What Are the Criteria for Selecting a Fintech Software Developer?
Selecting a reliable fintech software development service implies conducting an in-depth assessment of its reputation. While development agencies and hiring marketplaces often ask their most loyal customers to rate their work, having these reviews is still a positive signal, indicating that the agency is on good terms with its customers.In addition to reading reviews, we recommend that fintech companies contact notable clients of the development company and hear about their first-hand experiences working with the agency.
How Much Does It Cost to Hire a Fintech Developer?
It depends on the hiring platform and the hiring geography. In Ukraine, a contract blockchain engineer typically charges $70 per hour, while fintech app developer rates range from $50 to $60.Fintech developer hourly rates in the United States and Western Europe are higher, reaching around $100 and $80 per hour, respectively. The exception is software developers familiar with the Golang programming language, who charge an average of $137 per hour in the U.S.